The pressure to innovate quickly is real—but without compliance, growth can come at a cost. For organizations building software in highly regulated sectors like healthcare, finance, legal tech, and e-commerce, compliance standards such as HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PCI DSS are central to how data is collected, stored, processed, and secured.
What complicates matters is that many companies are now turning to external development partners—whether nearshore, offshore, or hybrid teams—to accelerate delivery. When you outsource parts of your engineering process, you don’t outsource responsibility. If your partner mishandles data or fails to meet compliance benchmarks, your company bears the risk.
This guide walks through how to maintain regulatory compliance throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC), especially when working with external vendors or nearshore teams.
What Does Compliance Mean in Software Development?
At its core, compliance in software development refers to building digital systems in accordance with relevant legal, industry, and security frameworks. It’s about ensuring that systems protect user data, enable transparency, and meet the standards set by governing bodies and regulators.
This can apply to:
- Backend infrastructure and cloud environments
- Application-level logic and code practices
- Third-party APIs and data pipelines
- Vendor access and engineering team behavior
For example:
- A telehealth platform must meet HIPAA and HITRUST controls around ePHI encryption and breach notifications
- A fintech app must comply with PCI DSS when handling payment data and maintain SOC 2 for trust assurance
- A global SaaS platform may need to comply with ISO 27001, GDPR, and various regional data laws
Compliance isn’t just a defensive move—it builds customer trust and opens doors to larger enterprise partnerships, where audits and vendor risk assessments are mandatory.
Key Compliance Standards You Should Know
Different industries have different requirements, but here are some of the most common compliance standards that may apply to your software project:
Key Compliance Standards You Should Know
In addition to global and industry-specific frameworks, companies working with development teams in Latin America should also account for local regulations. For example, Brazil enforces the Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), which mirrors GDPR in its focus on consent, transparency, and data minimization. Similarly, Colombia’s Habeas Data law protects personal data rights and imposes restrictions on how personal information can be stored and transferred. Other LATAM countries, including Chile and Mexico, are advancing similar data sovereignty and consent-focused mechanisms. These local frameworks are increasingly important when building products that store or process user data across borders.
How to Maintain Compliance Across the Development Lifecycle
Vendor Evaluation

Before you even sign a contract, evaluate your prospective partner’s compliance maturity:
- Have they worked in regulated industries before?
- Can they provide evidence of internal security practices—such as encryption policies, incident response plans, or audit logs?
- Do they use secure infrastructure (SOC 2, ISO 27001 certified clouds)?
- Are team members under NDA and access-restricted?
Ask for documentation. A reputable partner won’t hesitate to share past compliance audits, security whitepapers, or policy summaries. If a partner is vague or says “don’t worry, we’ve done this before,” take that as a red flag.
Contract Negotiation
Contracts are your first line of defense in ensuring compliance is enforceable, not just implied. Include:
- Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) that define roles, responsibilities, and breach processes
- Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) if working across borders (especially EU → LATAM)
- Confidentiality agreements for every developer with access to sensitive data
- IP and code ownership clauses, ensuring compliance with licensing and auditability
- Termination protocols outlining data deletion and offboarding procedures
Also consider adding right-to-audit clauses or requiring annual security certifications from your vendor.
Development
This is where compliance becomes tangible. What happens at the code level and in your delivery pipeline directly impacts whether or not you meet regulatory standards. Best practices include:
- Secure coding frameworks (e.g., OWASP Top 10, static analysis with tools like SonarQube)
- Least privilege access policies for GitHub, cloud consoles, and production environments
- Real-time logging of system access, changes, and user actions
- Two-factor authentication for code repos and production systems
- Use of vetted, up-to-date third-party packages to avoid vulnerabilities
- Developer training on compliance frameworks relevant to your industry
Development is also the right time to integrate privacy by design—ensuring user data is only collected when necessary and stored with consent.
Deployment and Maintenance
Many companies pass compliance audits during development but fail to maintain controls after release. Don’t let deployment become a blind spot. Your compliance controls should include:
- Immutable audit trails for deployments and access to production systems
- Encryption of both data in transit and at rest (TLS, AES-256)
- Secure CI/CD pipelines (signed commits, validated build artifacts)
- Continuous monitoring using tools like AWS CloudTrail, Datadog, or Splunk
- Regular vulnerability scanning and patching schedules
- Clear incident response protocols—including notification timelines, containment procedures, and post-mortems
You should also plan for annual compliance reviews—especially as your product scales or integrates new vendors, APIs, or regions.
👋 Worried about meeting compliance standards in your next software project?
We help companies build software with data privacy in mind—whether you’re targeting HIPAA, SOC 2, PCI DSS, or regional data laws.
Trusted by tech leaders at:



Compliance Considerations for Nearshore & LATAM Teams
Some companies are hesitant to involve LATAM development teams in compliance-sensitive projects—but that hesitation is often based on outdated assumptions. In reality, Latin America has:
- Rapidly growing tech ecosystems (Mexico, Brazil, Colombia, Chile)
- Developers with deep experience in HIPAA, PCI, SOC 2 environments
- Evolving national compliance laws that mirror GDPR and CCPA
That said, teams must still be vetted. Look for:
- Contractors working under legally binding agreements
- Developers with role-based access controls
- Infrastructure that complies with international standards
- Legal entities or employer-of-record setups to ensure tax and labor law compliance
Nearshoring can absolutely be compliant—it just requires a thoughtful approach.
Tech Stack Considerations: Build with Compliance in Mind
Compliance isn’t just about policies—it’s about architecture. Your tech stack should support your regulatory goals, not fight against them. Key tools and services:
- AWS/GCP/Azure with HIPAA, SOC 2, and PCI DSS support
- Identity & Access Management (IAM) platforms like Okta or Auth0
- Infrastructure as Code to version-control your environment and meet audit requirements
- Audit-ready logging platforms like Datadog, Sumo Logic, or Panther
- Compliance automation tools like Drata, Vanta, or Tugboat Logic
Documentation is also key: architecture diagrams, data flow maps, and user access matrices can save you hours during a compliance audit.
Common Compliance Pitfalls to Avoid
These are the mistakes that can derail your compliance efforts—often when you’re moving fast or scaling quickly:
- 🚫 Assuming a vendor’s platform is compliant without validating their controls
- 🚫 Using production data in staging or development environments
- 🚫 Ignoring country-specific laws when transferring user data across borders
- 🚫 Failing to rotate credentials and keys regularly
- 🚫 Overlooking shared responsibility in cloud environments (your cloud provider may be certified—but your application stack still needs to be secure)
Proactive documentation and internal training can eliminate many of these risks.
Compliance-First Development in Action
The most successful organizations build compliance into their development model:
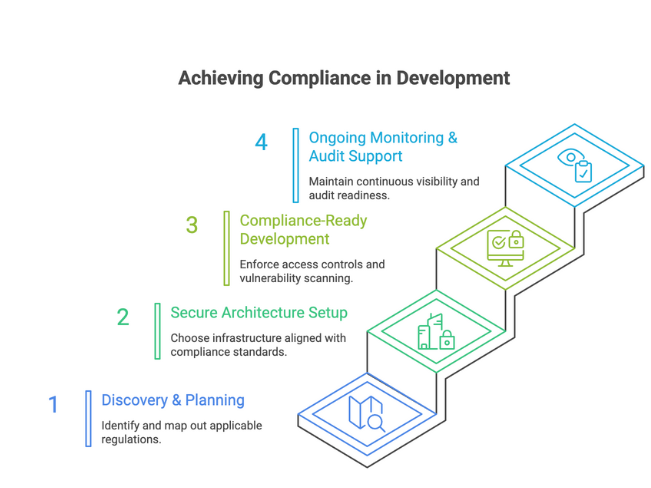
- Discovery & Planning
- Map out applicable regulations based on industry, geography, and user data types
- Secure Architecture Setup
- Choose infrastructure and workflows aligned with SOC 2, HIPAA, or ISO 27001
- Compliance-Ready Development
- Enforce access controls, logging, and vulnerability scanning from the start
- Ongoing Monitoring & Audit Support
- Maintain continuous visibility, alerts, and audit readiness through your operations lifecycle
When compliance is part of your process—not a scramble at the end—it creates speed, trust, and peace of mind.
In a world of rising data sensitivity and ever-tightening regulations, compliance isn’t just a requirement—it’s a market advantage. Whether you’re launching a healthcare app, building a payment system, or preparing for SOC 2 certification, aligning your development process with the right compliance strategy can unlock new customers, reduce risk, and improve operational resilience.
Ready to Build Compliance Into Every Stage of Your Project?
Curotec specializes in building software systems that meet HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and regional LATAM compliance frameworks. Whether you need a full build or a nearshore team that’s already audit-ready, we can help you deliver with confidence.
Let’s talk about your compliance goals.